5.1 Overview
Game Theory (GT) is a well-known branch in economic studies as a theoretical approach to model the strategic interaction between multiple individuals or players in a specific circumtance. GT can also be adopted in the scientific and engineering area, for instance, to optimize decision-making processes in a strategic setting. Moreover, GT has been successfully solved Multi-Agent Reinfrocement Learning (MARL) problems. If you would like to know more about the corporation between GT and MARL, you can have a look at these papers: (1) self-optimization using a State-based Potential Game approach and (2) potential game-based distributed optimization of a production unit.
MLPro-GT is developed as a sub-framework for the cooperative GT approach to solving MARL problems by inheriting a handful of main functionalities of MLPro-RL, such as the environment model, the agent model, and the environment-agent interaction model. This sub-framework foucuses on the cooperative GT approach on Markov games. A Markov game contains a group of independent players that make decisions simultaneuosly, see the figure below for overview.
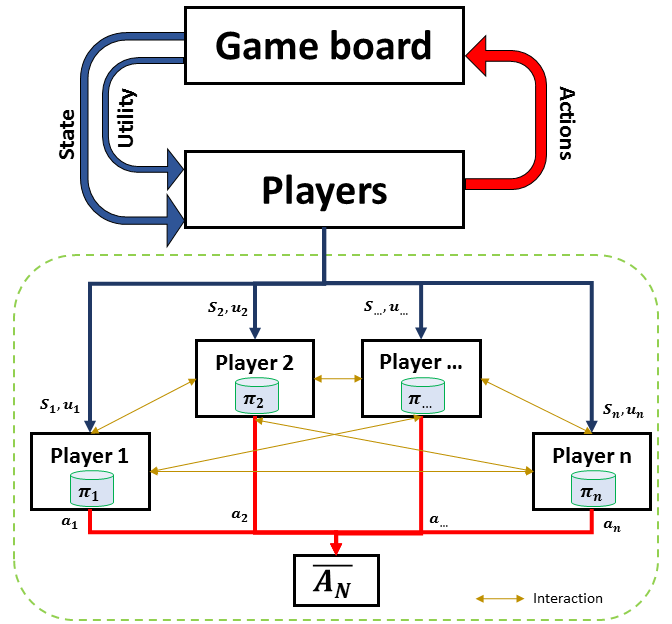
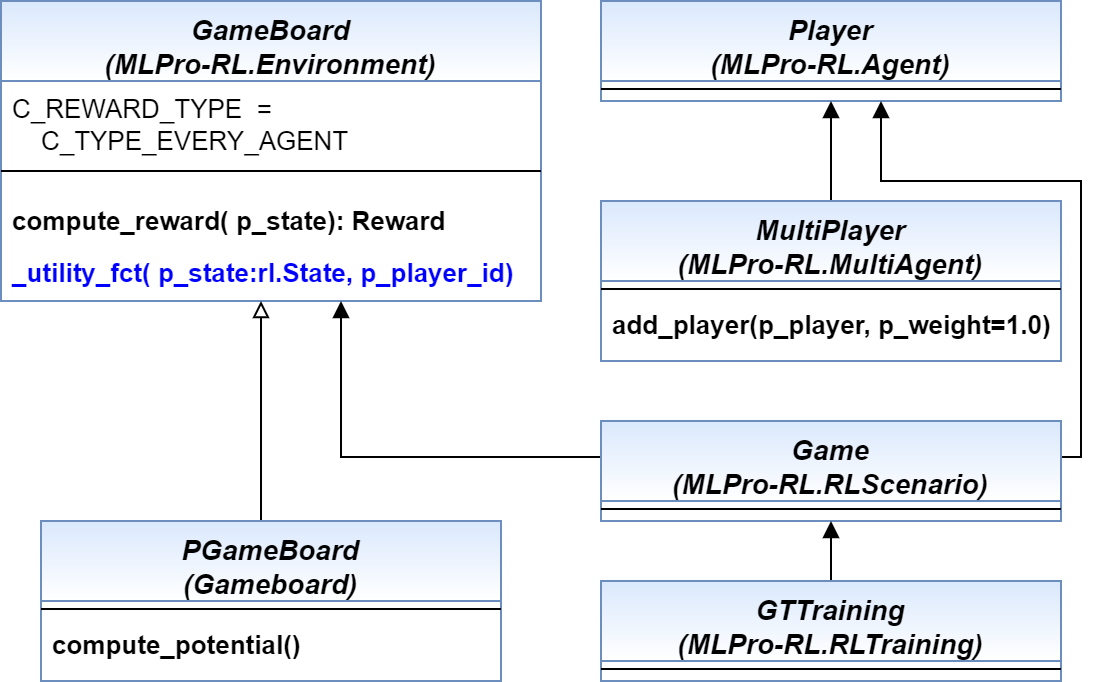
Additionally, you can find the more comprehensive explanations of MLPro-GT including a sample application and difference with a native RL approach in this paper: MLPro 1.0 - Standardized Reinforcement Learning and Game Theory in Python. The simplified diagram below shows the architecture of MLPro-GT, where MLPro-GT serves as a child package and MLPro-RL is its parent package.
If you are interested to utilize MLPro-GT, you can easily access the GT modules, as follows:
from mlpro.gt.models import *
You can also check out some of the examples on our how to files or here.