Custom Game boards
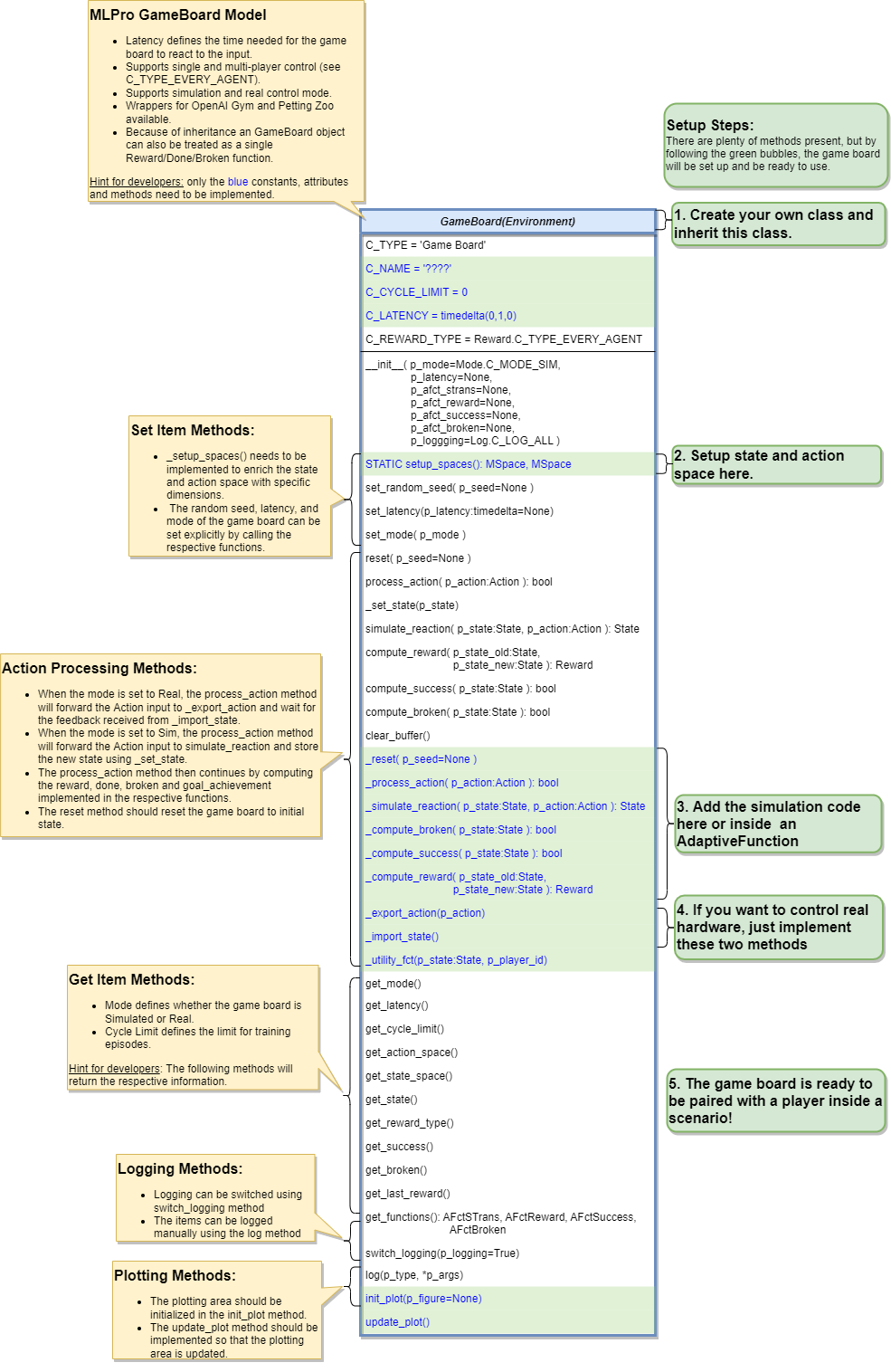
Game Board Creation for Simulation Mode
To create a game board that satisfies MLPro interface is immensly simple and straigtforward. Basically a MLPro game board is a class with several main functions. Each game board must apply the following mlpro functions:
from mlpro.gt.models import * class MyGameBoard(GameBoard): """ Custom game board that satisfies mlpro interface. """ C_NAME = 'MyGameboard' C_LATENCY = timedelta(0,1,0) # Default latency 1s C_REWARD_TYPE = Reward.C_TYPE_EVERY_AGENT # Default reward type def __init__(self, p_mode=C_MODE_SIM, p_latency:timedelta=None, p_logging=True): """ Parameters: p_mode Mode of environment (simulation/real) p_latency Optional: latency of environment. If not provided internal value C_LATENCY will be used by default p_logging Boolean switch for logging """ super().__init__(p_latency=p_latency, p_logging=p_logging) self._setup_spaces() self.set_mode(p_mode) def _setup_spaces(self): """ Static template method to set up and return state and action space of environment. Returns ------- state_space : MSpace State space object action_space : MSpace Action space object """ # Setup state space example # self.state_space.add_dim(Dimension('Pos', 'Position', '', 'm', 'm', [-50,50])) # self.state_space.add_dim(Dimension('Vel', 'Velocity', '', 'm/sec', '\frac{m}{sec}', [-50,50])) # Setup action space example # self.action_space.add_dim(Dimension('Rot', 'Rotation', '', '1/sec', '\frac{1}{sec}', [-50,50])) .... def _process_action(self, p_action: Action) -> bool: """ Custom method for state transition. To be implemented in a child class. See method process_action() for further details. Parameters ---------- p_action : Action Action to be processed Returns ------- success : bool True, if action processing was successfull. False otherwise. """ .... def _simulate_reaction(self, p_state: State, p_action: Action) -> State: """ Custom implementation to simulate a state transition. See method simulate_reaction() for further details. Parameters ---------- p_state : State Current state. p_action : Action Action. Returns ------- State Subsequent state after transition """ .... def _reset(self, p_seed=None) -> None: """ Custom method to reset the environment to an initial/defined state. Parameters ---------- p_seed : int Seed parameter for an internal random generator """ .... def _compute_reward(self, p_state_old: State, p_state_new: State) -> Reward: """ Custom reward computation method. See method compute_reward() for further details. Parameters ---------- p_state_old : State Optional state before transition. If None the internal previous state of the environment is used. p_state_new : State Optional tate after transition. If None the internal current state of the environment is used. Returns ------- Reward Reward object. """ .... def _compute_success(self, p_state: State) -> bool: """ Custom method for state evaluation 'success'. See method compute_success() for further details. Parameters ---------- p_state : State State to be assessed. Returns ------- bool True, if the given state is a 'success' state. False otherwise. """ .... def _compute_success(self, p_state: State) -> bool: """ Custom method for state evaluation 'success'. See method compute_success() for further details. Parameters ---------- p_state : State State to be assessed. Returns ------- bool True, if the given state is a 'success' state. False otherwise. """ .... def _utility_fct(self, p_state: State, p_player_id): """ Computes utility of given player. To be redefined. """ ....
One of the benefits for MLPro users is the variety of reward structures, which is useful for Multi-Agent GT and Game Theoretical approach. Three types of reward structures are supported in this framework, such as:
C_TYPE_OVERALL as the default type and is a scalar overall value
C_TYPE_EVERY_AGENT is a scalar for every agent
C_TYPE_EVERY_ACTION is a scalar for every agent and action.
To set up state- and action-spaces using our basic functionalities, please refer to our how to File 02 or here. Dimension class is currently improved and we will provide the explanation afterwards!
Game Board Creation for Real Hardware Mode
In MLPro, we can choose simulation mode or real hardward mode. For real hardware mode, the creation of an environment is very similar to simulation mode. You do not need to define _simulate_reaction, but you need to replace it with _export_action and _import_state as it is shown in the following:
def _export_action(self, p_action: Action) -> bool: """ Mode C_MODE_REAL only: exports given action to be processed externally (for instance by a real hardware). Please redefine. Parameters ---------- p_action : Action Action to be exported Returns ------- bool True, if action export was successful. False otherwise. """ raise NotImplementedError def _import_state(self) -> bool: """ Mode C_MODE_REAL only: imports state from an external system (for instance a real hardware). Please redefine. Please use method set_state() for internal update. Returns ------- bool True, if state import was successful. False otherwise. """ raise NotImplementedError
Game Board Checker
To check whether your developed game board is compatible to MLPro interface, we provide a test script using unittest. At the moment, you can find the source code here. We will prepare a built-in testing module in MLPro, show you how to excecute the testing soon and provides an example as well.